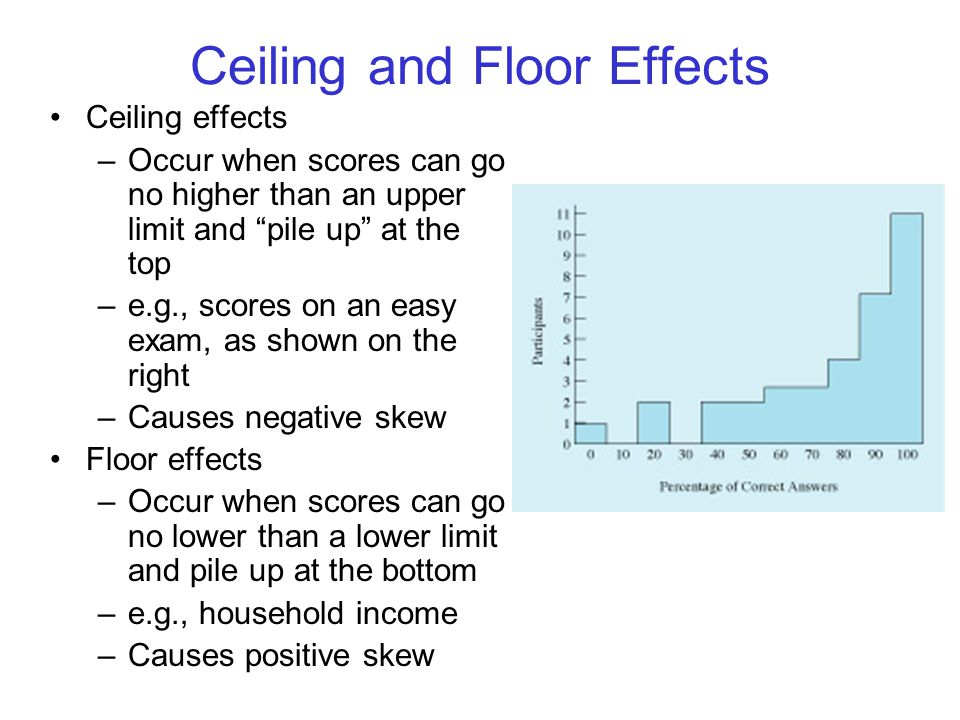
The term ceiling effect is a measurement limitation that occurs when the highest possible score or close to the highest score on a test or measurement instrument is reached thereby decreasing the likelihood that the testing instrument has accurately measured the intended domain.
Floor effect definition psychology.
Onsale alogia definition psychology and floor effect psychology download.
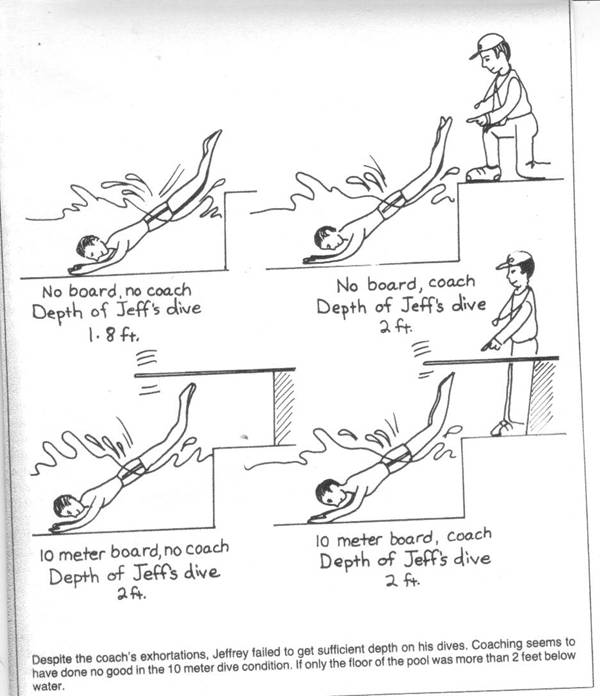
A floor effect is when most of your subjects score near the bottom.
Floor effects are occasionally encountered in psychological testing when a test designed to estimate some psychological trait has a minimum standard score that may not distinguish some test takers who differ in their responses on the test item content.
With other types if the subject doesn t know they aren t.
Ceiling effect is used to describe a situation that occurs in both pharmacological and statistical research.
For example the distribution of scores on an ability test will be skewed by a floor effect if the test is much too difficult for many of the respondents and many of them obtain zero scores.
In layperson terms your questions are too hard for the group you are testing.
This is even more of a problem with multiple choice tests.
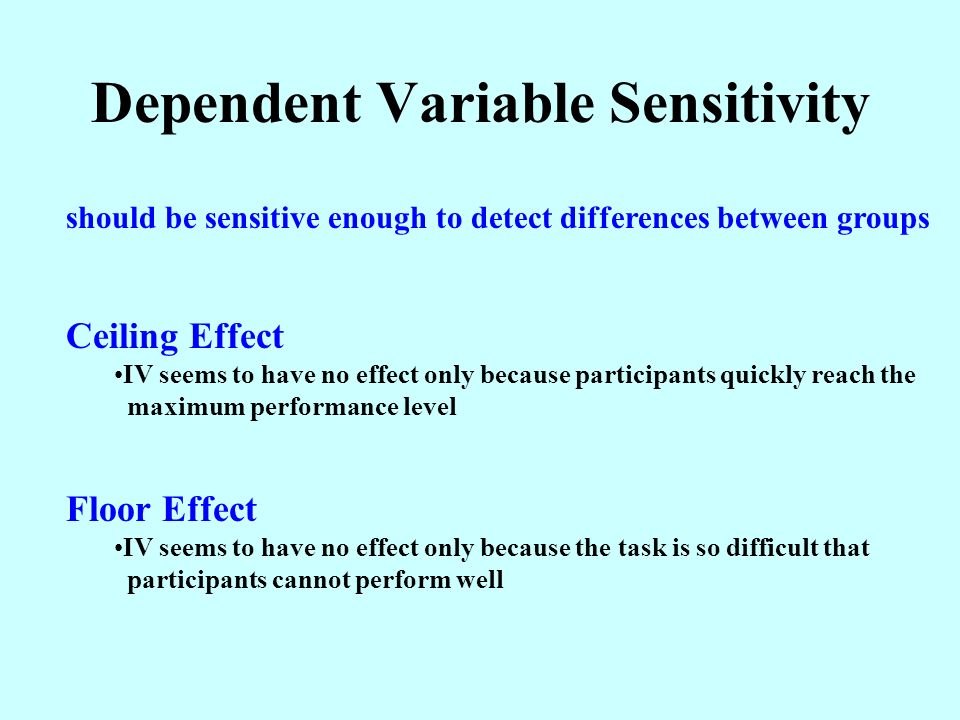
It essentially describes when the dependent variable has leveled.
In research a floor effect aka basement effect is when measurements of the dependent variable the variable exposed to the independent variable and then measured result in very low scores on the measurement scale.
Limited variability in the data gathered on one variable may reduce the power of statistics on correlations between that variable and another variable.
In pharmacology a ceiling effect is the point at which an independent variable which is the variable being manipulated is no longer affecting the dependent variable which is the variable being measured.
There is very little variance because the floor of your test is too high.
Ceiling effects and floor effects both limit the range of data reported by the instrument reducing variability in the gathered data.
A ceiling effect can occur with questionnaires standardized tests or other measurements used in research studies.
In statistics and measurement theory an artificial lower limit on the value that a variable can attain causing the distribution of scores to be skewed.
Psychology definition of floor effect.