Functions that create sas date datetime and time values the first three functions in this group of functions create sas date values datetime values and time values from the constituent parts month day year hour minute second.
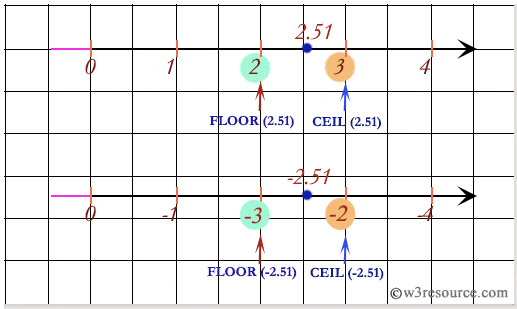
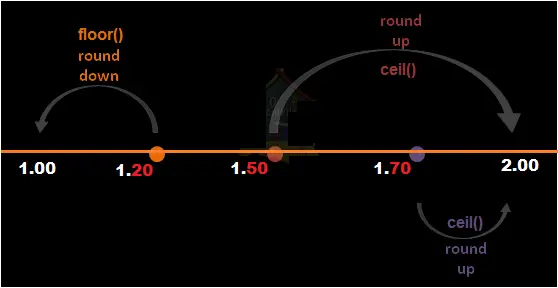
Floor function examples in sas.
Floor argument arguments argument is numeric.
This example uses the scan function to scan first and last names and output the names.
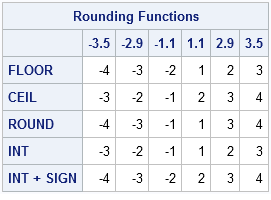
Floor function takes up the vector as an argument and rounds down all the values of that vector without decimal places so as no decimal values left floor function in r for vector floor c 1 234 2 342 4 562 5 671 12 345 14 567 output.
The floorz function uses zero fuzzing.
The following example shows positive numeric negative numeric and values with the floor function.
Sas statements results.
Floor function tree level 2.
Azure synapse analytics sql data warehouse and parallel data warehouse.
Following is the syntax for floor method.
The result is the integer part of the calculated value in the same data type as numeric expression.
If the argument is within 1e 12 of an integer the floor function fuzzes the result to be equal to that integer.
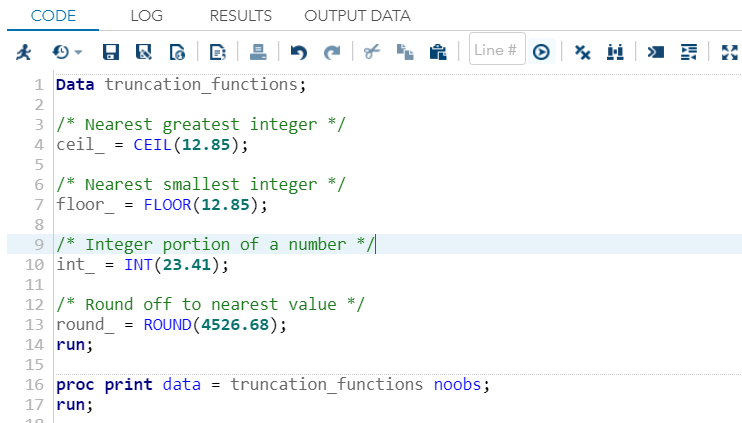
Use the floor function to round down the ratio to the nearest integer 3.
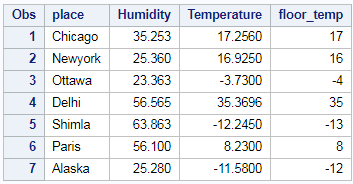
Some examples in this document use datalines in sas to create a data set using the cas engine.
And this is the ceiling function.
The floorz function does not fuzz the result.
Now let s get started.
The int function short for integer is like the floor function but some calculators and computer programs show different results when given negative numbers.
The mdy function can create a sas date value given a value for the month day and year.
Select floor 123 45 floor 123 45 floor 123 45.
Node 102 of 322.
Unlike the floorz function the floor function fuzzes the result.
For more information see functions in sas and cas.
Using the scan function in sas and cas.
Import math math floor x note this function is not accessible directly so we need to import math module and then we need to call this function using math static object.
X this is a numeric expression.
Therefore with the floorz function you might get unexpected results.
Example of floor function in r for a vector.
If the argument is within 10 12 of an integer the function returns that integer.
Multiply the result by 100 to restore the scale of the original number.
Some say int 3 65 4 the same as the floor function.
The floor function fuzzes the results so that if the results are within 1e 12 of an integer the floor function returns that integer.
Python number method floor returns floor of x the largest integer not greater than x.